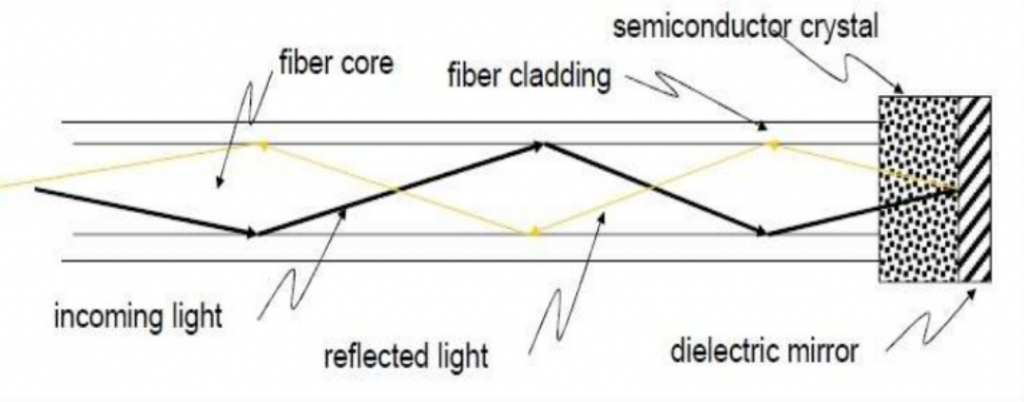
Fiber optic temperature sensors are designed to measure accurately temperature wherever typical temperature sensors could not be used. Semiconductor Bandgap technolgy is the main type of fiber optic temperature sensors. It consists of a gallium arsenide (GaAs) semiconductor crystal that is mounted on the end of an optical fiber. It works based on the effects of temperature variations on light transmission properties of GaAs. It is known that when the temperature increases, the GaAs transmission spectrum shifts to higher wavelengths.
The fiber optic temperature sensors have the following advantages:
- Electromagnetic interference (EMI) resistance
- Radio frequency interference (RFI) resistance
- Small measuring spot
- High temperature operating capability
- Cryogenic temperature operability
- Explosion proof